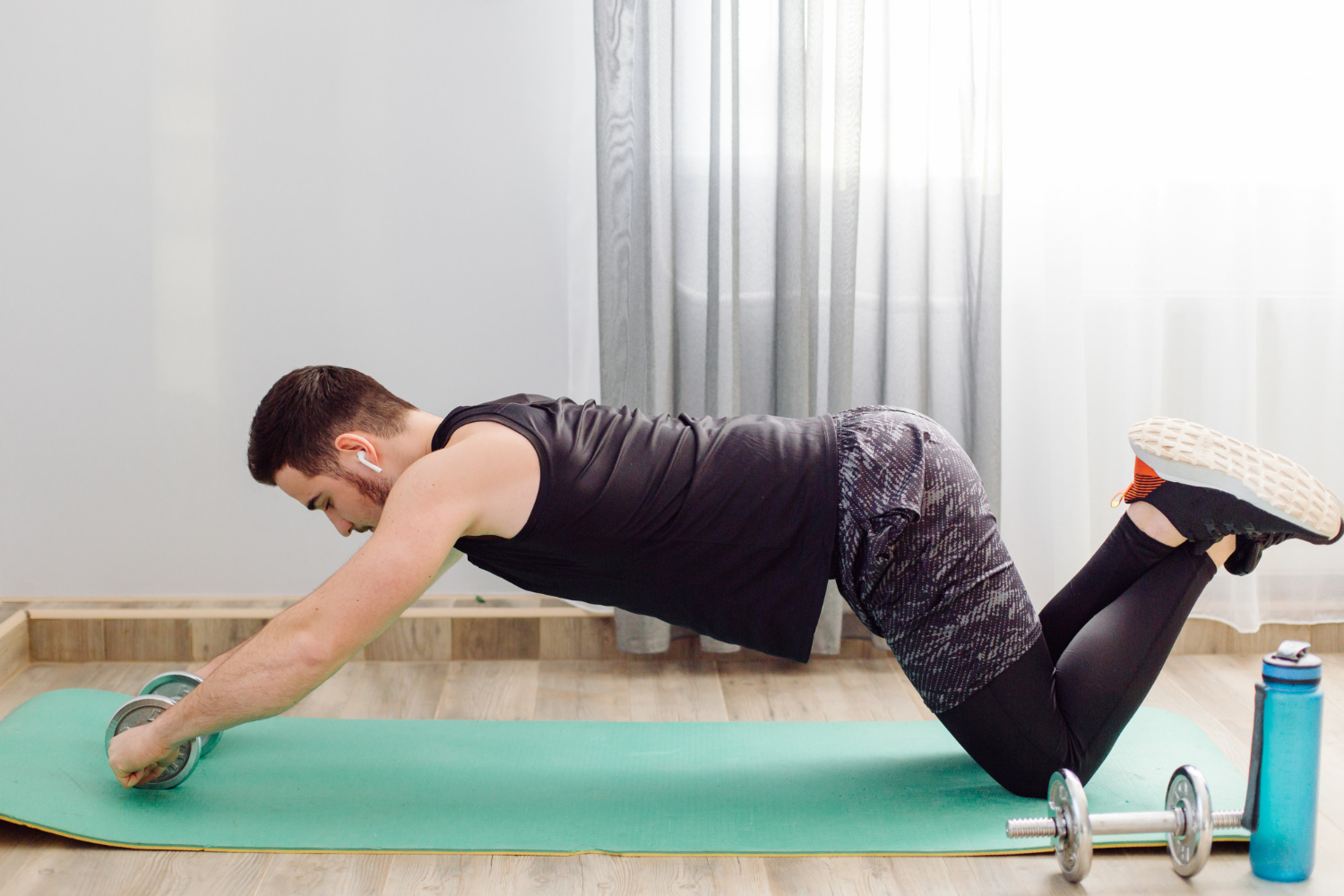
Groin strain is a common injury that occurs when the muscles in the groin area are stretched or torn. This type of injury is most often seen in athletes who participate in sports that require sudden movements or changes in direction, such as soccer, basketball and hockey. Other causes of groin strain can include overuse, muscle fatigue and improper warm up or stretching before activity. Risk factors for groin strain include previous injury, poor flexibility and muscle imbalances. Symptoms of groin strain can include pain, swelling and difficulty walking or moving the affected leg. Treatment for groin strain typically involves rest, ice, compression and elevation of the affected area, as well as physical therapy and stretching exercises to help prevent future injury.
Top Exercises to Relieve Groin Strain.
Groin strains can be quite painful and limiting, but luckily there are several exercises that can help alleviate the discomfort and promote healing. These exercises are designed to gently stretch and strengthen the muscles surrounding the groin area, improving flexibility and reducing strain. Here are some effective exercises to relieve groin strain:
1. Seated Groin Stretch.
Sit on the floor with your legs extended in front of you. Bend one knee and place the sole of your foot against the inner thigh of the opposite leg. Slowly lean forward, reaching towards your toes, until you feel a gentle stretch in your groin. Hold this position for 20-30 seconds and then switch sides.
2. Butterfly Stretch.
Sit on the floor and bring the soles of your feet together, allowing your knees to drop out to the sides. Hold onto your ankles or feet with your hands and gently press your knees down towards the floor. Maintain this stretch for 20 to 30 seconds while breathing deeply.
3. Adductor Squeeze.
Lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Place a small ball or pillow between your knees. Squeeze the ball or pillow using your inner thigh muscles, holding the contraction for a few seconds before releasing. Repeat this exercise for 10 to 15 repetitions.
4. Standing Groin Stretch.
Stand with your feet wider than shoulder-width apart. Slowly shift your weight to one side, bending that knee and keeping the other leg straight. Lean your torso towards the bent knee, feeling a stretch in the inner thigh of the straight leg. Hold for 20 to 30 seconds and then switch sides.
5. Hip Flexor Stretch.
Kneel on one knee with the other leg in front, bent at a 90-degree angle. Lean forward slightly, keeping your back straight, until you feel a stretch in the front of the hip and groin of the kneeling leg. Hold for 20 to 30 seconds and then switch sides.
6. Clamshell Exercise.
Lie on your side with your knees bent and feet together. Keeping your feet touching, lift your top knee as high as you comfortably can, while keeping your hips stacked. Slowly lower the knee back down. Repeat this movement for 10 to 15 repetitions on each side.
7. Wall Squats.

Stand with your back against a wall and your feet shoulder-width apart. Slowly slide your back down the wall, bending your knees until they are at a 90-degree angle. Hold this position for 10 to 20 seconds, then push through your heels to stand back up. Repeat for 10 to 15 repetitions.
| 💡 Tips FreakToFit.com Remember to start with gentle movements and gradually increase the intensity and duration of the exercises as your groin strain improves. If you experience any pain or discomfort during these exercises, it is important to stop and consult with a healthcare professional. |
Exercises To Avoid in Groin Strain.
When dealing with a groin strain, it is crucial to avoid exercises that can exacerbate the injury and hinder the healing process. Here are some exercises that should be avoided:
1. Squats.
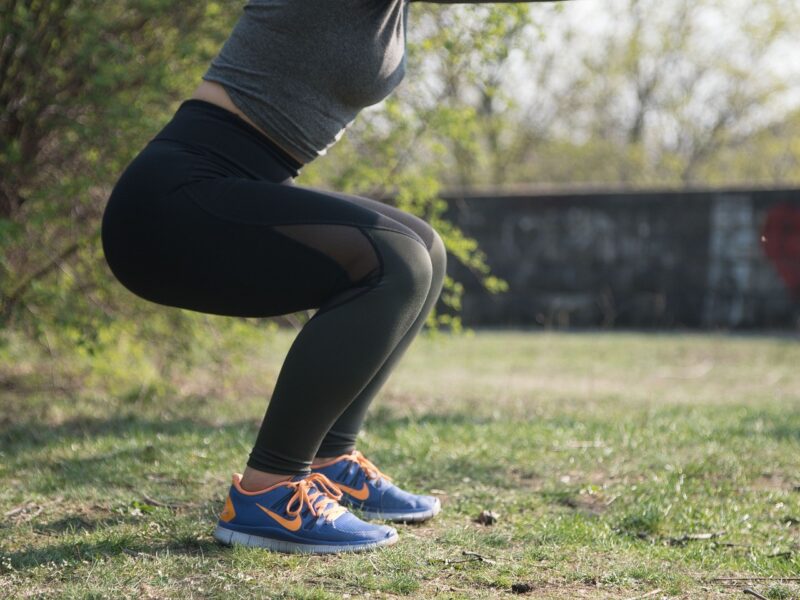

Squatting places significant strain on the groin muscles, making it one of the exercises to steer clear of during the recovery period. The deep flexion and extension movements required in squats can further strain the already injured area, leading to more pain and potential setbacks.
2. Lunges.

Similar to squats, lunges involve a significant range of motion and can put excessive stress on the groin muscles. The sudden change of direction and the need to stabilize the body during lunges can worsen the strain, prolonging the healing process.
3. Jumping exercises.
Plyometric exercises, such as box jumps or jumping jacks, should be avoided as they involve explosive movements that can strain the groin muscles. The impact and sudden changes in direction can hinder the recovery process and increase the risk of reinjury.
4. High-intensity interval training (HIIT).
HIIT workouts often involve quick and intense movements, which can strain the groin muscles. Movements like burpees, mountain climbers or squat jumps can put excessive pressure on the injured area, impeding healing and potentially causing more harm.
5. Leg presses.

Leg presses, especially those performed with heavy weights, can place substantial stress on the groin muscles. The pushing motion involved in leg presses can aggravate the strain, making it essential to avoid this exercise until the injury has fully healed.
6. Abdominal exercises that strain the groin.
Certain abdominal exercises, such as leg raises or bicycle crunches, can engage the groin muscles and cause discomfort. These exercises often require lifting the legs or twisting the torso, which can put unnecessary strain on the injured area.
7. Running or sprinting.
The repetitive impact of running or sprinting can strain the groin muscles, potentially leading to reinjury. It is advisable to avoid these activities until the groin strain has healed completely to prevent setbacks and promote a successful recovery.
| 💡 Tips FreakToFit.com Remember, every groin strain is unique and it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist to determine which exercises to avoid based on the severity and specific characteristics of the injury. Following their guidance will allow for a safe and effective recovery process. |
Prevention tips During exercises for groin strain.
Prevention tips during exercises for groin strain involve a combination of proper warm-up, adequate stretching and gradual progression in intensity. Here are some specific tips to help prevent groin strain during exercise:
1. Warm-up.
Prior to any exercise session, it is crucial to warm up your muscles properly. Engage in light cardiovascular exercises such as jogging or cycling for at least 5 to 10 minutes. This helps to increase blood flow to the muscles and prepares them for the upcoming activity.
2. Stretching.
Perform dynamic stretches that target the muscles around the groin area. These stretches should be done in a controlled manner and should not be painful. Focus on exercises that involve gentle movements, such as leg swings or hip circles to increase flexibility and range of motion.
3. Gradual progression.
When starting a new exercise or increasing the intensity of your workout, it is important to do so gradually. Avoid sudden, excessive movements or overloading the muscles around the groin area. Gradually increase the duration, frequency or intensity of your exercises over time, allowing your body to adapt and strengthen the muscles gradually.
4. Correct form and technique.
Ensure proper form and technique during exercises. Incorrect posture or technique can put undue stress on the groin muscles, leading to strain. Seek guidance from a qualified professional, such as a trainer or physical therapist, to learn the correct form and technique for exercises that involve the groin area.
5. Strengthening exercises.
Incorporate specific strengthening exercises to target the muscles around the groin area. Exercises like squats, lunges and bridges can help to improve the strength and stability of the groin muscles, reducing the risk of strain.
6. Rest and recovery.
Allow adequate rest and recovery time between exercise sessions. This helps to prevent overuse injuries, including groin strain. Listen to your body and avoid pushing through pain or discomfort. If you experience any signs of strain, such as pain or swelling, take a break from exercising and allow the muscles to heal.
7. Supportive gear.
Consider wearing supportive gear, such as compression shorts or groin braces, during exercises that involve high impact or sudden changes in direction. These can provide additional stability and support to the muscles around the groin area.
8. Cross-training.
Incorporate a variety of exercises into your routine to avoid overloading the same muscles repeatedly. By cross-training and engaging in different activities, you can reduce the risk of overuse injuries, including groin strain.
| 💡 Tips FreakToFit.com Remember, prevention is key when it comes to groin strain during exercise. By implementing these tips, you can minimize the risk of injury and ensure a safe and effective workout routine. If you have any concerns or persistent pain, consult with a healthcare professional for further evaluation and guidance. |
Bottom Line.
Exercises for groin strain are essential for the proper rehabilitation and recovery of the affected area. These exercises help to strengthen the muscles surrounding the groin area, increase flexibility and reduce the risk of future injuries. It is crucial to perform these exercises under the guidance of a healthcare professional and to gradually increase the intensity and duration of the workouts. With consistency and patience, individuals can effectively overcome a groin strain and return to their daily activities and sports with confidence.

 Workout
Workout
 Meditation
Meditation


 Stories
Stories


 Podcast
Podcast E-book
E-book