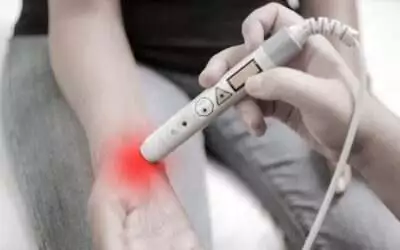
Wounds, whether resulting from surgical procedures, accidents, or underlying medical conditions, require meticulous care and attention. Over the years, the medical community has made significant advancements in understanding the complexities of the wound healing process. As a result, new technologies and methodologies have emerged to improve outcomes, reduce complications, and enhance patient comfort.
In the not-so-distant past, wound care was limited to gauze, antiseptics, and, in some cases, stitches. Fast forward to today, and we find ourselves at the nexus of innovation, with cutting-edge approaches that seem straight out of science fiction. These novel therapies not only expedite recovery but also minimize scarring and other associated risks.
Biological Wound Dressings.
One of the most notable advancements in wound care is the development of biological dressings. Unlike traditional dressings, these are derived from living organisms and can include materials such as collagen, hyaluronic acid, and even cultured skin cells. These dressings provide a moist environment conducive to healing, reduce inflammation, and promote the growth of healthy tissue.
Smart Wound Monitoring.
With the integration of technology into healthcare, smart bandages have emerged. These are embedded with tiny sensors that can monitor parameters like pH levels, temperature, and moisture—factors that play a pivotal role in the healing process. If any irregularities are detected, the smart bandage can alert healthcare professionals, ensuring timely interventions.
Oxygen and Hyperbaric Therapy.
Oxygen is a crucial element in the wound healing process. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) involves having patients breathe pure oxygen in a pressurized room or chamber. This process increases the oxygen level in the blood, promoting faster healing, reducing the risk of infections, and improving blood flow to wound areas.
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT).
NPWT, also known as a vacuum-assisted closure, is a therapeutic technique that employs a vacuum to remove blood or serous fluid from a wound, promoting healing. It reduces swelling, stimulates granulation tissue formation, and keeps the wound environment moist.
Stem Cell Therapy.
Regenerative medicine, especially stem cell therapy, holds significant promise in wound care. By introducing stem cells to the wound site, the body is encouraged to regenerate lost tissue faster, enhancing the healing process. While still in its nascent stages, preliminary results from various studies are encouraging.
Role of Wound Care Products in Modern Treatment.
The market has seen an influx of advanced wound care products that cater to specific wound types and stages of healing. From antimicrobial dressings that ward off infections to hydrogel dressings that maintain optimal moisture, these products are at the forefront of modern wound care. Given their efficacy and ease of application, many healthcare professionals are integrating these advanced solutions into their therapeutic regimens.
Laser Therapy for Wound Management.
Laser therapy uses specific wavelengths of light to stimulate healing, reduce pain and inflammation, and enhance tissue repair. It’s a non-invasive procedure that’s particularly beneficial for patients with chronic wounds or those who aren’t ideal candidates for surgical interventions.
Nanotechnology in Wound Care.
Nanotechnology has paved the way for microscopic treatments with macro impact. Nano-sized particles can deliver drugs directly to wound sites, ensuring targeted treatment. This precision reduces side effects and accelerates healing, showcasing the potential of nanomedicine in revolutionizing modern wound care approaches.
Revolutionizing Recovery: The New Era of Wound Care.
The landscape of wound healing has undergone radical transformations in recent years. What once relied heavily on rudimentary methods now harnesses the power of biology, technology, and advanced wound care products. As research continues and technologies evolve, there’s no doubt that we will witness further breakthroughs in this field. For patients and healthcare professionals alike, these advances promise improved outcomes, reduced recovery times, and a brighter future for wound care.










































 Workout
Workout

 Meditation
Meditation



 Podcast
Podcast
 E-book
E-book