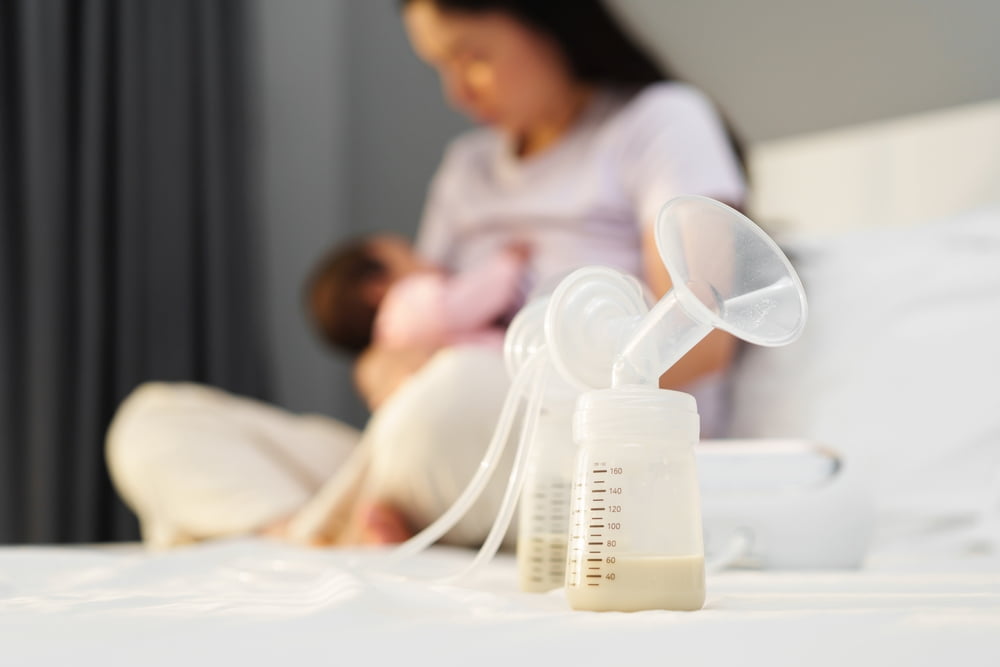
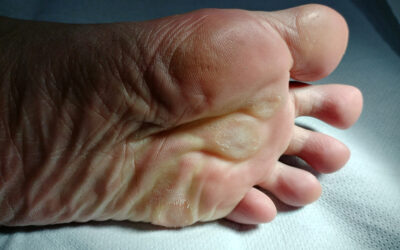
If you or someone you know has eczema, you know how frustrating it can be to find a treatment that actually works. Eczema is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by dry, itchy and inflamed patches of skin. While there are many over the counter and prescription treatments available, some people are turning to natural remedies, including breast milk.
Breast milk has been used for centuries as a natural remedy for various ailments, including eczema. In this article, we will explore the science behind breast milk and eczema, how to use breast milk for eczema, benefits, risks, precautions to take and other natural remedies for eczema.
How Does Breast Milk Work for Eczema?
Breast milk is a natural, nutrient-rich food that is produced by the mammary glands of female mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for infants and provides them with all the necessary vitamins, minerals and antibodies they need to grow and develop. Breast milk is also incredibly versatile and has been used for centuries as a natural remedy for various ailments.
Breast milk contains a variety of components that make it an effective treatment for eczema. One of these components is immunoglobulin A (IgA), which is a type of antibody that helps to fight off infections. IgA is found in high concentrations in breast milk and can help to reduce inflammation and prevent infections of the skin.
Breast milk also contains a variety of other proteins, including lactoferrin, lysozyme and immunoglobulin G (IgG), which have antibacterial and antimicrobial properties. These proteins help to prevent the growth of harmful bacteria and reduce the risk of infection.
The Science Behind Breast Milk and Eczema.
Studies have shown that breast milk can be an effective treatment for eczema. One study published in the International Journal of Dermatology found that applying breast milk to the skin of infants with eczema helped to improve their symptoms. The study found that breast milk reduced the severity of eczema and improved the overall condition of the skin.(1)
Another study published in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology found that breast milk contains high levels of lipids, which can help to repair the skin barrier and reduce inflammation. The study also found that breast milk can help to stimulate the growth of healthy skin cells which can help to improve the overall condition of the skin.(2)
Benefits of Using Breast Milk for Eczema.
Here are eight benefits of using breast milk for eczema:
1 Natural Moisturizer.
Breast milk contains natural oils and fats that act as an effective moisturizer for dry and eczema prone skin. Applying breast milk topically can help to soothe and hydrate the affected areas, reducing itchiness and promoting healing.
2 Anti-Inflammatory Properties.
Breast milk is packed with anti inflammatory compounds, including cytokines and immunoglobulins, which help to calm the skin’s immune response. These properties can alleviate the redness and swelling associated with eczema, providing relief and comfort.
3 Immune Boosting Properties.
Breast milk is known for its immune boosting properties due to its high concentration of antibodies. When applied to eczema prone skin, these antibodies can help to strengthen the skin’s natural defense mechanisms which reducing the risk of infections and promoting faster healing.
4 Antibacterial and Antifungal Action.
Breast milk contains antimicrobial components such as lysozyme and lactoferrin, which possess antibacterial and antifungal properties. These properties can help to combat the colonization of harmful bacteria and fungi on the skin, preventing secondary infections and improving overall skin health.
5 Gentle on Sensitive Skin.

Breast milk is gentle and easily tolerated by sensitive skin, making it an ideal option for babies and individuals with eczema. Unlike some commercial skincare products, breast milk is free from harsh chemicals, fragrances and additives that may exacerbate eczema symptoms.
6 Cost Effective Solution.
Using breast milk for eczema is a cost effective solution compared to expensive creams and medications. Breast milk is readily available and does not require any additional purchases, making it an accessible and affordable option for those seeking relief from eczema symptoms.
7 Emotional Bonding.
Applying breast milk to an infant’s eczema can foster emotional bonding between the mother and child. The act of gently massaging the breast milk onto the affected areas provides comfort, reassurance and a nurturing touch, which can have a positive impact on both the physical and emotional well being of the child.
8 Holistic Approach.
Utilizing breast milk for eczema aligns with a holistic approach to healthcare, as it harnesses the natural healing properties of breast milk to address the root causes of the condition. This approach focuses on promoting overall wellbeing and supporting the body’s innate ability to heal itself.
*Note. While breast milk may not be a cure all for eczema, it offers numerous benefits that can complement existing treatments and provide relief for individuals suffering from this challenging condition. As always, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating breast milk or any alternative remedies into your eczema management plan.
How to Use Breast Milk for Eczema?
1 Cleanse the affected area.
Before applying breast milk, gently cleanse the eczema affected skin with a mild, fragrance free cleanser. This step helps to remove any impurities or irritants, providing a clean surface for the breast milk to work its magic.
2 Express breast milk.
Begin by expressing some fresh breast milk into a clean container. Ensure that your hands are thoroughly washed to maintain hygiene during the process.
3 Test for allergies.
Perform a patch test by applying a small amount of breast milk on a small area of unaffected skin. Wait for about 24 hours to check for any adverse reactions or allergies. If no reaction occurs, proceed to the next step.
4 Apply breast milk.
Using a clean cotton ball or a sterilized dropper, gently apply a thin layer of breast milk onto the eczema affected areas. Make sure to cover the entire affected region, ensuring that the milk is evenly distributed.
5 Allow it to air dry.
After applying breast milk, allow it to air dry naturally. This will allow the active components present in breast milk to penetrate the skin and provide relief from eczema symptoms.
6 Repeat the process.
For optimal results, repeat this process multiple times throughout the day. The frequency of application can vary depending on the severity of the eczema and the individual’s response to breast milk treatment.
7 Observe changes.
Keep a close eye on the affected area to monitor any improvements or changes. Breast milk’s antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and moisturizing properties can help to reduce redness, soothe itching and promote healing.
8 Complement with other treatments.
While breast milk can be effective in managing eczema, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for a comprehensive treatment plan. They may recommend additional remedies or prescribe medicated creams to complement the use of breast milk.
9 Maintain a healthy lifestyle.

Alongside using breast milk, maintaining a healthy lifestyle is crucial in managing eczema. Ensure proper hydration, a balanced diet rich in nutrients and avoid triggers such as harsh soaps, allergens and excessive stress.
10 Monitor and seek professional advice.
If eczema symptoms persist or worsen despite using breast milk, it is essential to consult a dermatologist or a healthcare provider. They can provide expert guidance, diagnose underlying causes, and recommend suitable treatments.
*Note. Remember, while breast milk has shown promising results in managing eczema, it may not work for everyone. Each individual’s response to treatment can vary, so it is essential to find the approach that works best for you or your child’s specific condition.
Other Natural Remedies for Eczema.
While there are various medical treatments available, many individuals seek alternative natural remedies to help manage their eczema symptoms. Here are some additional natural remedies that can potentially provide relief:
1 Coconut Oil.
Known for its moisturizing properties, coconut oil can help to alleviate dryness and reduce itchiness associated with eczema. Applying virgin coconut oil directly to the affected areas can provide a protective barrier, locking in moisture and minimizing irritation.
2 Aloe vera.
With its soothing and anti inflammatory properties, aloe vera gel is often used to calm irritated skin. Extracting the gel directly from an aloe vera plant and applying it to eczema patches can help to reduce redness, itchiness and promote healing.
3 Tea tree oil.
Recognized for its antimicrobial and anti inflammatory effects, tea tree oil may be beneficial for managing eczema symptoms. Diluting a few drops of tea tree oil with a carrier oil such as coconut or olive oil and applying it topically can help to reduce inflammation and prevent infection.
4 Oatmeal Baths.
Taking regular baths with colloidal oatmeal can provide relief for eczema prone skin. Oatmeal has anti inflammatory properties that can soothe itchiness and help to restore the skin’s moisture balance. Adding a cup of finely ground oatmeal to a warm bath and soaking for 15 to 20 minutes can alleviate symptoms.
5 Honey.
Raw honey possesses antibacterial and anti inflammatory properties, making it a potential natural remedy for eczema. Applying a thin layer of honey to affected areas, allowing it to sit for a few minutes and rinsing it off with lukewarm water can help to soothe and moisturize the skin.
6 Evening primrose oil.
Derived from the evening primrose plant, this oil contains gamma-linolenic acid (GLA), an omega-6 fatty acid known for its anti-inflammatory effects. Taking evening primrose oil capsules orally may help to reduce eczema symptoms by improving skin hydration and reducing itchiness.
7 Calendula.
Calendula also known as marigold, has been used traditionally to treat various skin conditions, including eczema. Its anti-inflammatory and wound healing properties can promote skin repair and alleviate itching. Applying calendula cream or ointment to affected areas can provide relief.
*Note. Remember, while these natural remedies have shown promise in managing eczema symptoms for some individuals, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional or dermatologist before trying them, especially if you have severe eczema or if you’re currently using prescribed medications.
Risks and Precautions When Using Breast Milk for Eczema.
When considering the use of breast milk for eczema treatment, it is important to be aware of the potential risks and take necessary precautions. While breast milk has been known to provide various health benefits, including its potential to alleviate eczema symptoms, there are certain factors to consider to ensure safe and effective usage.
1 Allergic Reactions.
Although rare, it is possible for a baby to be allergic to components present in breast milk, such as proteins or other substances. Before using breast milk for eczema treatment, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional who can assess the potential risk of allergic reactions and guide accordingly.
2 Contamination.
Breast milk can become contaminated with bacteria or viruses if proper hygiene measures are not followed during expression, storage or handling. To minimize the risk of contamination, it is crucial to adhere to strict hygiene practices, such as washing hands thoroughly before expressing or handling breast milk, utilizing sterilized containers for storage and ensuring proper refrigeration or freezing methods.
3 Inadequate Nutritional Value.
Depending solely on breast milk for eczema treatment may not provide sufficient nutritional requirements for the baby. Breast milk is primarily designed to meet the nutritional needs of infants and while it may have potential benefits for eczema, it should not replace a well balanced diet or any prescribed medications.
4 Variability in Composition.
The composition of breast milk can vary from mother to mother and even within the same mother at different times. This variability may affect the consistency and effectiveness of using breast milk for eczema treatment. Therefore, it is essential to monitor the response of the baby’s skin to breast milk and consult with a healthcare professional if any concerns arise.
5 Infection Transmission.
If a mother has any infectious diseases, there is a possibility of transmitting them through breast milk. It is crucial for mothers to disclose their medical history and undergo necessary testing to prevent the transmission of infections to the baby.
6 Lack of Scientific Evidence.
While anecdotal evidence suggests that breast milk may provide relief for eczema symptoms, there is limited scientific research specifically addressing this topic. It is important to understand that using breast milk for eczema is not a proven or guaranteed solution and consulting with a healthcare professional is essential to explore other available treatment options.
*Note. To ensure the safe and effective use of breast milk for eczema treatment, it is highly recommended to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a dermatologist or paediatrician. They can provide personalized guidance, assess potential risks and help to develop an appropriate treatment plan that includes breast milk, if deemed suitable.
Testimonials and Success Stories.
Many people have reported success in using breast milk to treat eczema. One mother shared her experience on Reddit, saying, “My son had severe eczema and we tried everything, including prescription medications. Nothing worked until we started using breast milk. Within a few days, his eczema was significantly improved.”
Another person shared their experience on a parenting forum, saying, “I have been using breast milk to treat my eczema for a few weeks now and the results have been amazing. My skin is less inflamed and itchy and the overall condition has improved.”
Bottom Line.
The question of whether breast milk heals eczema remains a topic of debate and requires further research. While some studies and anecdotal evidence suggest that breast milk may have beneficial properties for soothing eczema symptoms, the limited scientific evidence available is inconclusive. It is important to note that eczema is a complex condition influenced by various factors, including genetics, allergens and immune system responses. Therefore, seeking medical advice and exploring other proven treatment options alongside breastfeeding is crucial for effectively managing eczema in infants and children. Further research and clinical trials are needed to determine the true efficacy of breast milk in healing eczema and to provide clearer guidance for parents and healthcare professionals.
+2 Sources
Freaktofit has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, educational research institutes, and medical organizations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and up-to-date by reading our editorial policy.
- Efficacy of topical application of human breast milk on atopic eczema healing among infants: a randomized clinical trial; https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25640116/
- Long-chain saturated fatty acids in breast milk are associated with the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis via induction of inflammatory ILC3s; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8222289/











































 Workout
Workout

 Meditation
Meditation



 Podcast
Podcast
 E-book
E-book