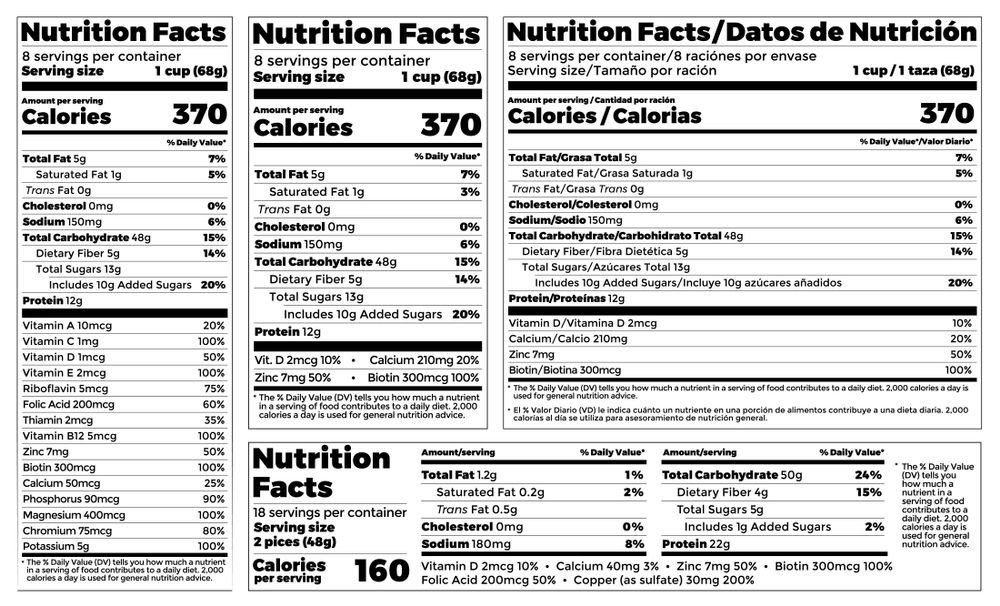
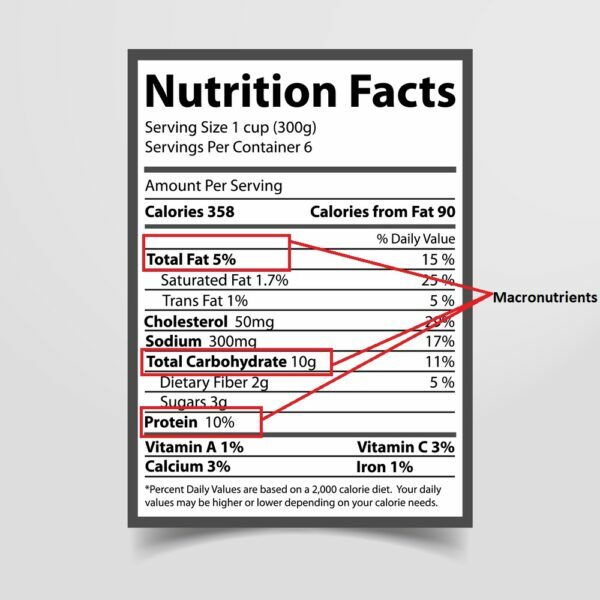
The macronutrients are carbohydrates, proteins & fats and they are each located on different parts of the nutritional label. To help you understand where you should look to find them on your nutrition label, here’s a breakdown of the three macronutrients and what part of the label they appear on.
Where Are the Macronutrients Located on a Nutritional Label?
The macronutrients are located in the following order from top to bottom:- Total fat, Saturated fat, Cholesterol, Sodium, Potassium, Carbohydrates and Dietary fiber.
There are also two rows of micronutrients: Vitamins and Minerals.
The vitamins are found to the right of sodium and potassium while minerals are found below carbohydrates.
Importance of Carbohydrates.
Carbohydrates are one of the three macronutrients. What does this mean? Well, in short, carbs are an important part of your diet because they provide energy to our bodies.
They also help regulate blood sugar and have been shown to be beneficial for heart health. Carbohydrates can be found in whole grains, cereals, starchy vegetables like potatoes or corn, legumes like beans and lentils, fruits like bananas or apples, and dairy foods like milk or yogurt. These are all excellent sources of carbohydrates.
Importance of Protein.
Protein is one of three major macronutrients and is important for growth, maintenance, and repair of cells. It is made up to form amino acids that are used to build muscle tissues, regulate hormones and enzymes, form neurotransmitters, help with memory formation and repair damaged tissues.
Itcan be found in animal sources such as poultry, eggs, fish or meat; or in plant sources such as beans and nuts. The recommended intake for protein per day varies from 0.36 grams per pound of body weight (0.8 grams per kilogram) for sedentary adults to 0.66 grams per pound of body weight (1.2 grams per kilogram) for active individuals who exercise regularly while undertaking regular physical activity throughout the day.
Importance of Fat.
Fat is an essential nutrient for our bodies and is used in many bodily functions. Fat provides energy, helps with growth and development, protects organs from injury, and carries fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K).
It also slows down absorption of glucose into the bloodstream so it can be used for energy instead of being stored as fat. A healthy diet should contain about 20% to 35% calories from fat.(1)
When looking at a nutritional label on food packaging, look at the grams of total fat per serving to see if it falls within this range.
Bottom Line.
The macronutrient information is located at the top of each column, to the left of where it says % Daily Value. The three macronutrients are protein, carbohydrates and fats. Protein is found in animal foods like chicken and eggs. Carbohydrates are found in things like fruits, vegetables, grains and milk. Fats come from meats and dairy as well as some oils.
+1 Source
Freaktofit has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, educational research institutes, and medical organizations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and up-to-date by reading our editorial policy.
- A healthy approach to dietary fats: understanding the science and taking action to reduce consumer confusion; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5577766/








































 Workout
Workout

 Meditation
Meditation



 Podcast
Podcast
 E-book
E-book